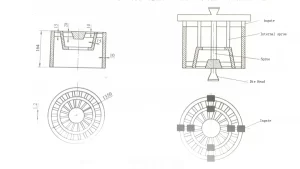
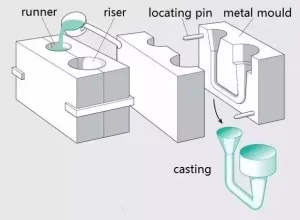
Gravity die casting is a semi-permanent or permanent mold casting process in which molten metal is injected from a container into a mold without using any force other than gravity, and the filling can be controlled by tilting the mold angle. Both metal and sand cores can be incorporated into components to increase design complexity. This method allows a set of molds to be reused indefinitely to produce the same part.
It is ideal for the production of repeatable medium- and high-volume parts and is used for parts that are slightly heavier, larger in size, and have higher structural requirements than high-pressure die-casting.
Gravity die casting requires lower mold costs than high pressure die casting, but is more durable than sand casting, which uses steel molds. A mold is a permanent shape that consists of two parts.
Gravity Die Casting Processes
Benefits of Gravity Die Casting
Gravity die casting, also known as permanent mold casting, is a casting process that involves pouring molten metal into a reusable mold under the force of gravity. This method offers several advantages in the manufacturing industry. Here are some benefits of gravity die casting:
1. High Quality and Dimensional Accuracy:
Gravity die casting produces parts with excellent surface finish, high dimensional accuracy, and tight tolerances. The use of a permanent mold helps maintain consistent part dimensions, resulting in precise and repeatable casting outcomes.

2. Cost-Effective:
Gravity die casting is a cost-effective casting method, especially for high-volume production. The reusable molds used in this process can withstand multiple casting cycles, reducing the need for frequent mold replacements. This leads to lower tooling costs and overall production expenses.
3. Improved Mechanical Properties:
Gravity die casting allows for the production of parts with improved mechanical properties. The controlled cooling process in the mold helps in achieving a fine-grained microstructure, which enhances the strength and durability of the castings.
4. Versatility in Material Selection:
Gravity die casting can be used with a wide range of materials, including aluminum, magnesium, zinc, and copper alloys. This versatility allows manufacturers to choose the most suitable material for their specific application requirements.
5. Reduced Porosity:
Gravity die casting produces castings with minimal porosity. The controlled filling of the mold cavity under gravity helps minimize the formation of air pockets and gas entrapment, resulting in denser and more structurally sound castings.
6. Faster Production Cycle:
Gravity die casting offers a relatively faster production cycle compared to other casting methods. The molten metal is poured directly into the mold, and the solidification process is accelerated by the controlled cooling in the mold. This allows for quicker production turnaround times.
7. Enhanced Design Flexibility:
Gravity die casting allows for complex and intricate part designs to be easily cast. The permanent molds can be designed with intricate details and features, enabling the production of intricate and aesthetically pleasing castings.
In summary, gravity die casting offers high-quality castings with excellent dimensional accuracy, cost-effectiveness, improved mechanical properties, versatility in material selection, reduced porosity, faster production cycles, and enhanced design flexibility. These advantages make gravity die casting a popular choice in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods manufacturing.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Gravity Die Casting Manufacturers
There are several factors to consider when choosing gravity die casting manufacturers:
- Experience and Expertise: Look for manufacturers with extensive experience and expertise in gravity die casting. Experienced manufacturers are more likely to produce high-quality products.
- Quality Assurance: Check if the manufacturer has a quality assurance program in place. This ensures that the products meet the required standards and specifications.
- Equipment and Technology: Choose a manufacturer with modern equipment and technology. This helps to ensure that the casting process is efficient and accurate.
- Capacity: Check the capacity of the manufacturer. This is important if you need to produce a large volume of products.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the manufacturing process. Compare the costs of different manufacturers to find one that offers competitive pricing.
- Location: Consider the location of the manufacturer. You may want to choose a manufacturer that is located close to your business to reduce shipping costs and lead times.
- Communication: Choose a manufacturer with good communication skills. This ensures that you can communicate your requirements effectively and get updates on the progress of your order.
Industries We Serve for Gravity Die Casting
There are various industries use gravity die casting. Some examples include:
- Automotive Industry: Gravity die casting is commonly used in the automotive industry to manufacture engine parts, transmission components, and suspension system parts.
- Aerospace Industry: Gravity die casting is used to produce components such as turbine blades, engine casings, and structural components.
- Medical Industry: Gravity die casting is used to produce medical equipment such as surgical instruments, dental implants, and prosthetic devices.
- Electrical Industry: Gravity die casting is used to manufacture electrical components such as transformer housings, switchgear components, and electrical enclosures.
- Construction Industry: Gravity die casting is used to produce components such as door handles, locks, and hinges.
- Agricultural Industry: Gravity die casting is used to manufacture parts for tractors, harvesters, pump casting, and other agricultural machinery.
- Marine Industry: Gravity die casting is used to produce components such as propellers, gearboxes, and steering systems for boats and ships.
Co-worked with Customers Use Gravity casting parts

Chapter 1
Gravitational Casting Process Solutions
1.1-Selection of Molding (Core) Method for a Gravity Die Casting Manufacturer
Molding (core) is the most basic process in gravity casting, usually divided into manual molding, core manufacturing and machine modeling, core manufacturing.
1.1.1 Hand molding and core making
1.1.2 Machine styling and core making
Machine modeling and core production rate is high, low labor intensity, the quality of gravity casting parts is stable, but requires complex process equipment, production preparation time is long, so machine modeling and core manufacturing mainly used for the mass production of gravity casting parts.
1.2-Selection of Mold Types
The casting molds of gravity casting are mainly divided into four types: wet mold, dry mold, surface dry mold, and self hardening mold. The selection of each casting mold needs to be determined based on factors such as the weight, structure, and quality requirements of gravity casting parts, production batch size, and workshop production conditions.
When the gravity casting is too high and the static pressure of the metal exceeds the compressive strength of the wet mold, dry sand mold or self hardening sand mold should be considered.
When placing a large amount of cold iron inside the mold, wet molds should be avoided. Due to the rusting or cooling of the cold iron, water droplets may condense and cause porosity defects after pouring. If it is necessary to use cold iron, it should be preheated in advance and poured into the mold in a timely manner after being placed in the mold.
Gravity cast parts that require a long molding process or a long waiting time for pouring should not be wet molded, as placing the wet mold for too long will air dry, reduce surface strength, and are prone to sand flushing defects.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions that a gravity die casting manufacturer may receive:
Gravity die casting can be used with a variety of materials, including aluminum, copper , zinc, and magnesium alloys. Iron casting, Stainless steel casting are also OK to do.
The maximum size of a part that can be produced using gravity die casting varies depending on the manufacturer’s equipment and capabilities. However, it is typically limited to parts with a maximum weight of around 50 kg.
Gravity die cast parts typically undergo a finishing process that includes trimming excess material, surface treatments such as sandblasting or polishing, and coating or painting.
The lead time for gravity die casting production depends on the complexity of the part, the quantity needed, and the manufacturer’s production schedule. It is best to consult with the manufacturer directly to get an accurate estimate.
The minimum order quantity for gravity die casting varies depending on the manufacturer’s policies and capabilities. Some manufacturers may have a minimum order quantity of 100 pieces, while others may be able to accommodate smaller orders.
Gravity die casting is known for its accuracy and consistency in producing complex shapes with a smooth surface finish. It is generally more efficient and cost-effective than other casting methods such as sand casting, but may not be suitable for producing large or intricate parts that require other methods such as investment casting.