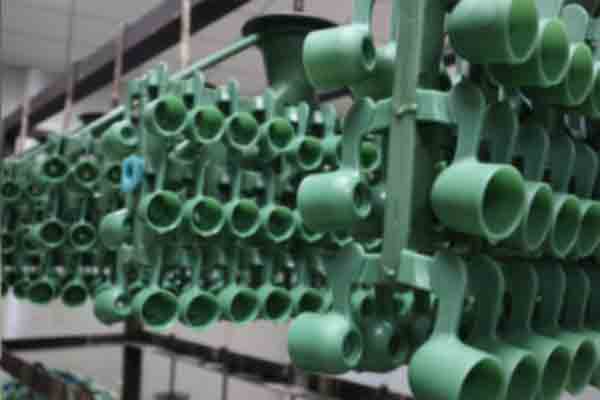
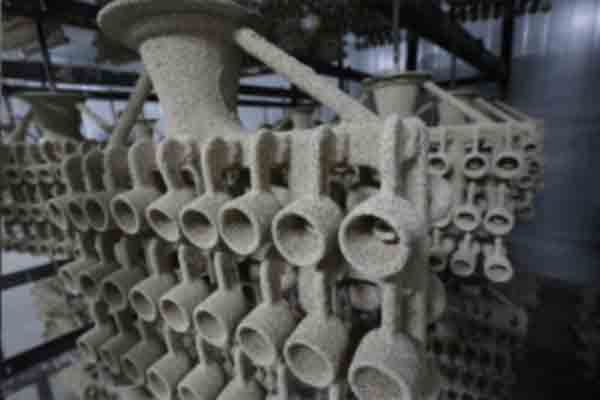
Medical Investment Casting
Investment casting is a popular manufacturing process used to create high-quality medical equipment. The process involves pouring molten metal into a mold, allowing it to solidify, and removing the mold to reveal the finished product. Investment casting can produce complex shapes and intricate details that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using other methods. Investment casting is ideal for producing small to medium-sized medical equipment with complex shapes and high precision. Some examples of medical equipment that can be manufactured using investment casting include surgical instruments, dental implants, orthopedic implants, and prosthetic limbs.
We are a Chinese manufacturer of medical machinery products, committed to providing customized medical machinery casting and processing services for customers in various fields: diagnosis, health monitoring devices, research, beauty instruments, medical electronic devices, and many other medical equipment.
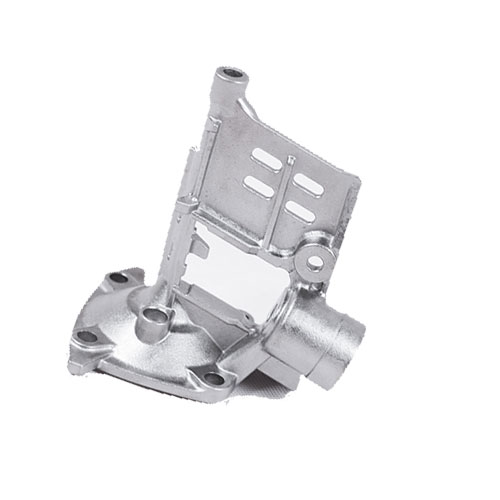

Investment casting Medical equipment parts
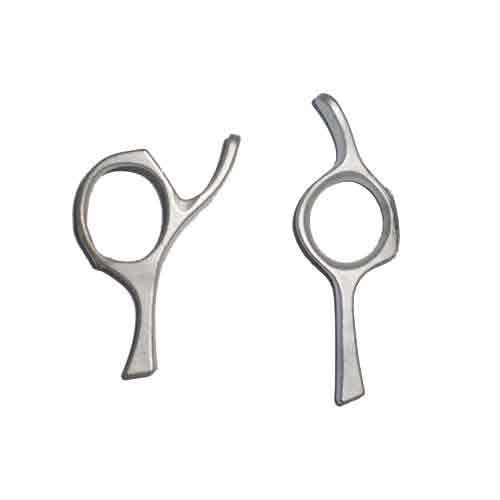

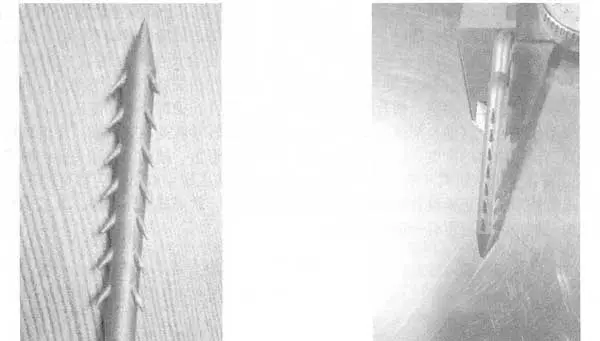
Medical scissors casting
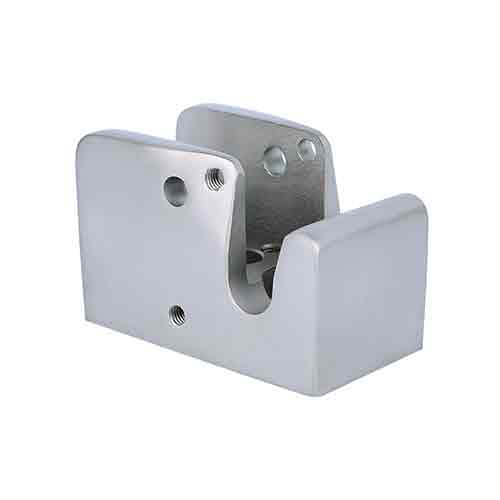

Medical equipment components
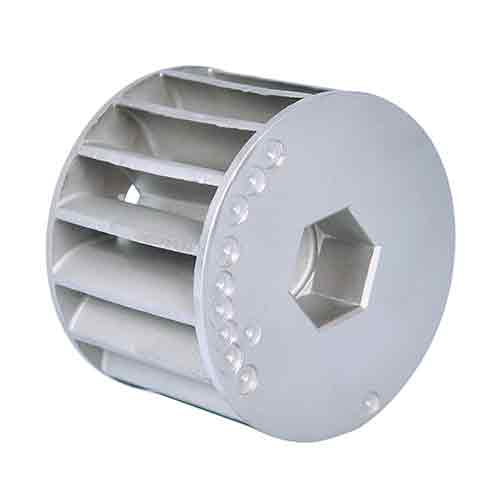

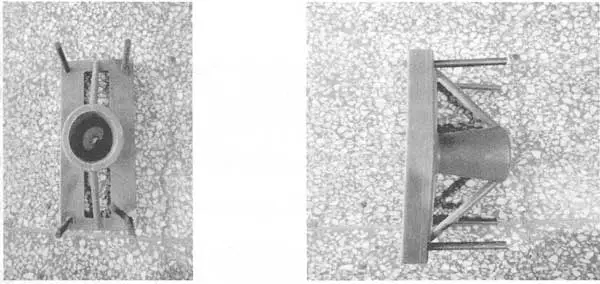
Medical investment casting roller
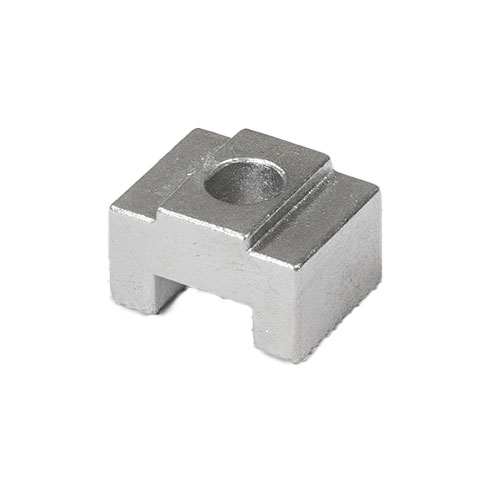

Medical investment fittings casting
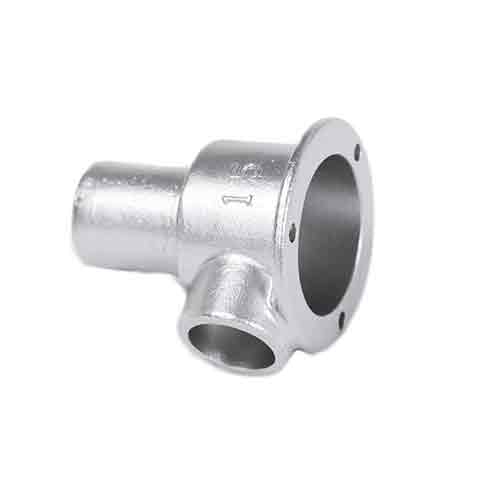

Stainless steel Medical equipment casting
Medical equipment investment casting Processes
Medical equipment investment casting involves several steps, including:
Advantages of investment casting in medical equipment manufacturing

– Investment casting is known as precision casting, so it has high precision and accuracy
– Ability to produce complex shapes and intricate details
– Consistency of part quality and dimensions
– Minimal machining required after casting
– Lower material waste compared to other manufacturing methods